Semantic reinforcement for better understanding
Semantic reinforcement for better understanding
We help humans understand large language model outputs faster, more clearly, and with reduced cognitive load.
A post-generation semantic restructuring layer — no model changes required.
the product
A semantic interpretation reinforcement layer, not an interface.
Navia-X is not:
a conversational AI
a browser extension focused on convenience
a standalone interface competing with existing models
What this is not
What it is
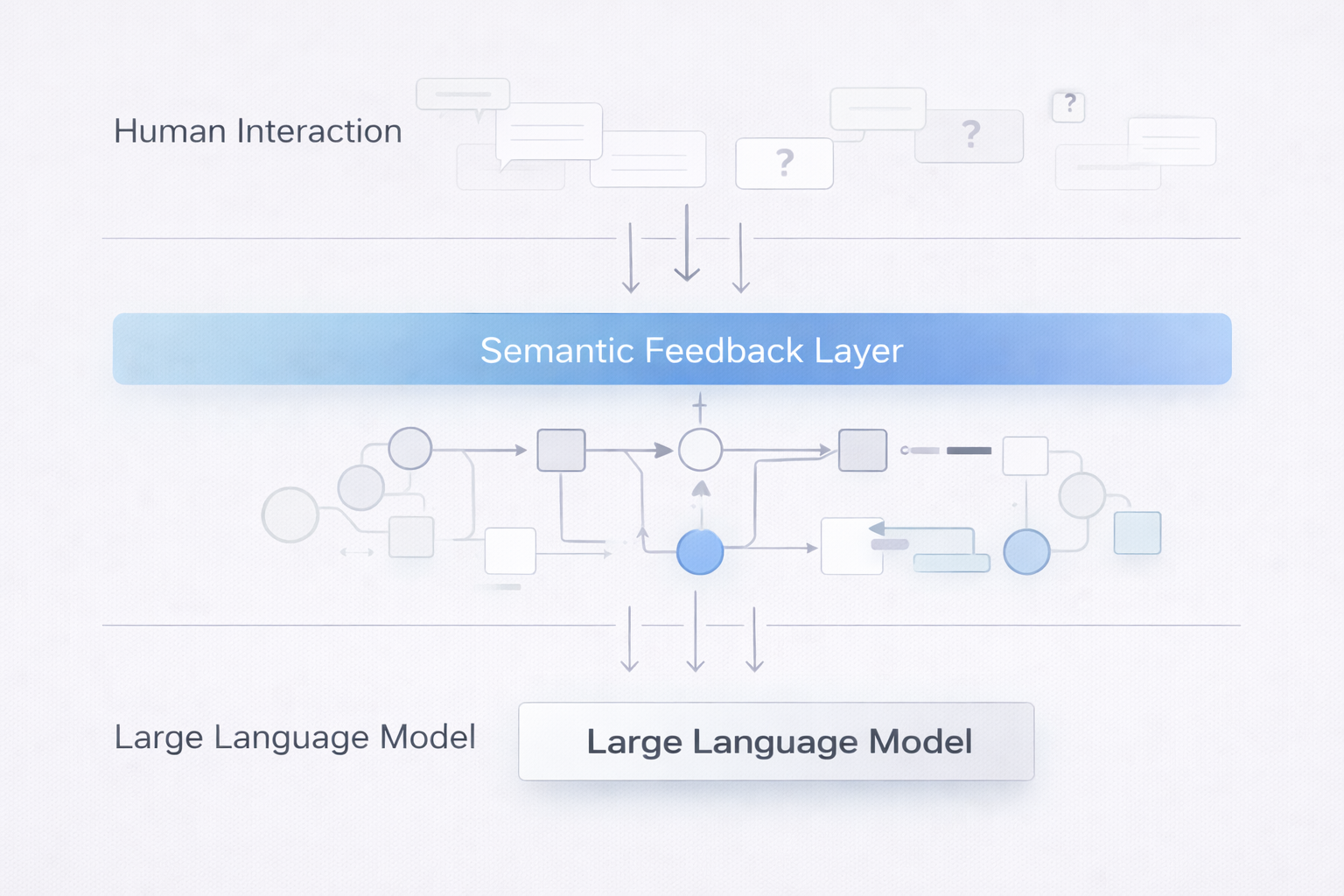
Navia-X delivers a semantic interpretation reinforcement layer that runs alongside large language model interfaces.
It enables users to clarify unclear concepts in-context, while structuring those moments of misunderstanding as machine-readable semantic signals.
Current status
Live MVP · Actively iterating · Model-agnostic
how it works
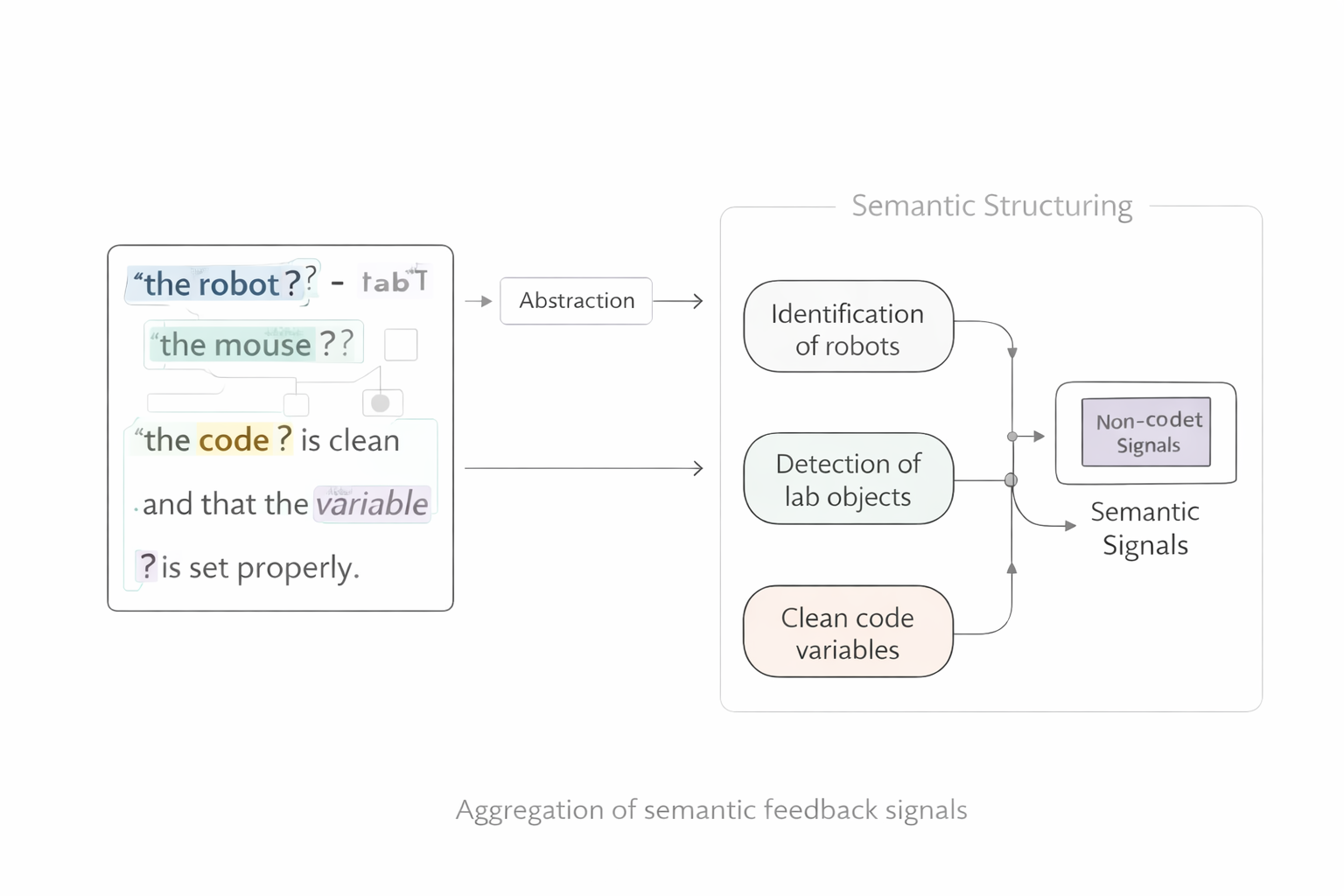
1. In-Context Interpretation
Users highlight or hover over unclear words, phrases, or concepts during interaction.
Interpretation occurs directly within the original context, without leaving the primary interface.
Each interaction is abstracted into structured semantic signals:
No raw content dependency
No personal data required
No persistent user profiling
2. Semantic Structuring
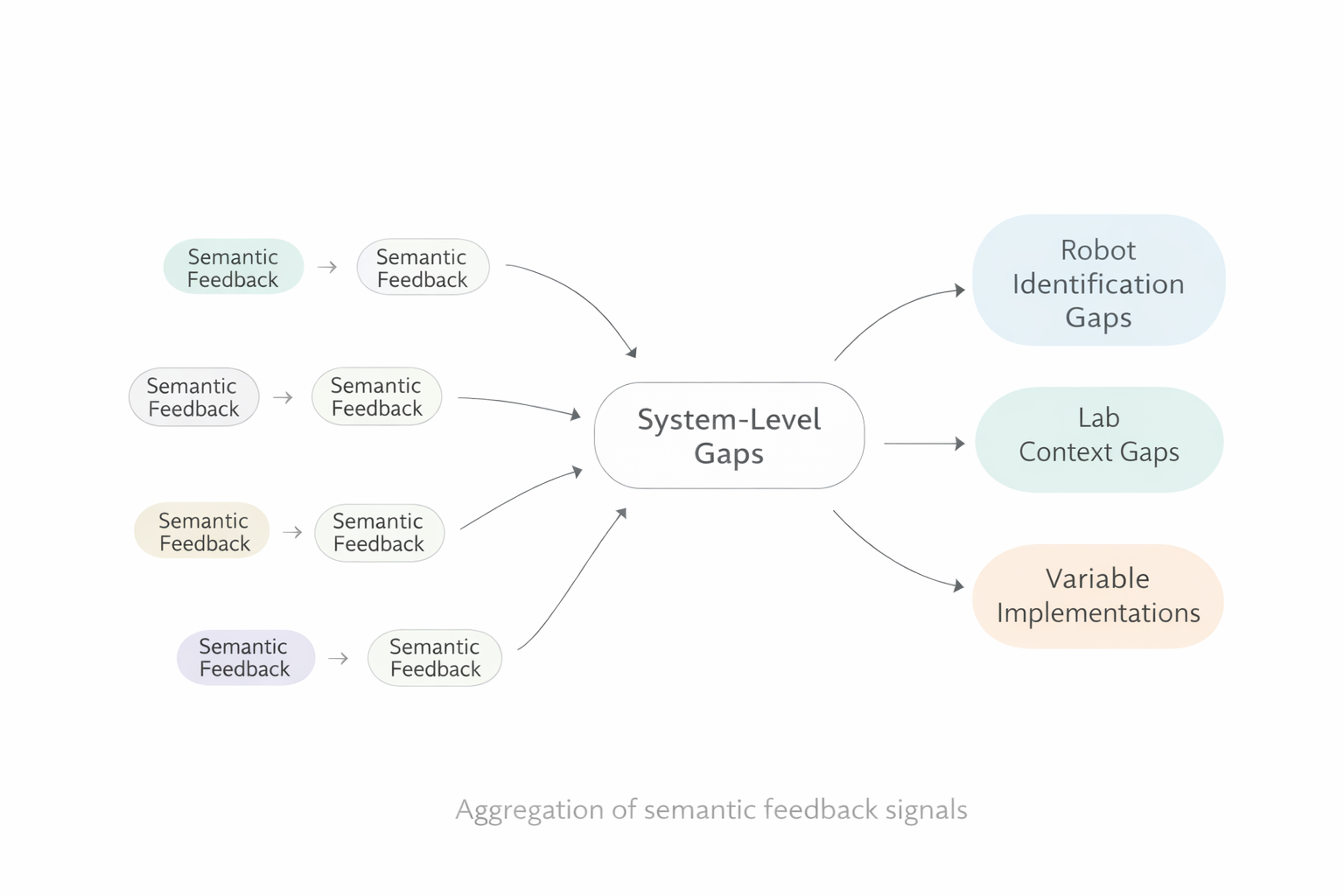
Structured understanding gaps are aggregated at a system level, forming a semantic feedback layer that reflects where human interpretation consistently breaks down.
3. Signal Aggregation
Illustrative diagrams only. The semantic layer operates independently of any interface.
feedback to models
The problem
Large language models see prompts and outputs.
They rarely see misunderstanding.
Our approach
Navia-X structures interpretation failures as:
non-privacy
non-content
semantic feedback signals
These signals describe how and where users struggle to understand model outputs — not what they asked or received.
What we don’t do
No claims of model retraining
No access to model weights
No black-box optimization
Positioning
Navia-X operates adjacent to models, not inside them.
Supportive, not competitive.
Designed to improve alignment and interpretability through real usage signals.
explorations
Current focus
Semantic interpretation reinforcement — actively developed and iterated.
Exploring
Questions around identity, continuity, and reasoning in AI systems, approached as long-term research directions, not near-term product commitments.
This page reflects conceptual continuity, not a delivery roadmap.